Attention: the stuff/information you need is at the beginning, Most of the stuff that follow the practical section you will not need (The some theory section), whatever more you see is for my reference, for the curious, and for those who are wondering why i do it this way.
The lowdown: I have successfully repaired my 2014 (3rd gen) Prius battery, despite the fact that most information on rebuilding your Prius battery online is Bull, almost as if it were engineered so that you kill the remaining good cells after a month or two.
Update Dec, 10 2024: The battery was rebuilt somewhere around the end of COVID, probably 2021 or early 2022 (Yes, i really don’t remember), it is still working perfectly on a car that commutes 200KMs per day, 5 days a week, besides its daily town use, proving beyond any doubt (in my mind) that i was right, YOU PAIR SIMILARLY HEALTHY BATTERIES AND DO NOT CONNECT WEAK BATTERIES WITH HEALTHY ONES, THE ADVICE ON THE INTERNET IS THE OPPOSITE OF WHAT YOU SHOULD DO…. Why this is follows in this post
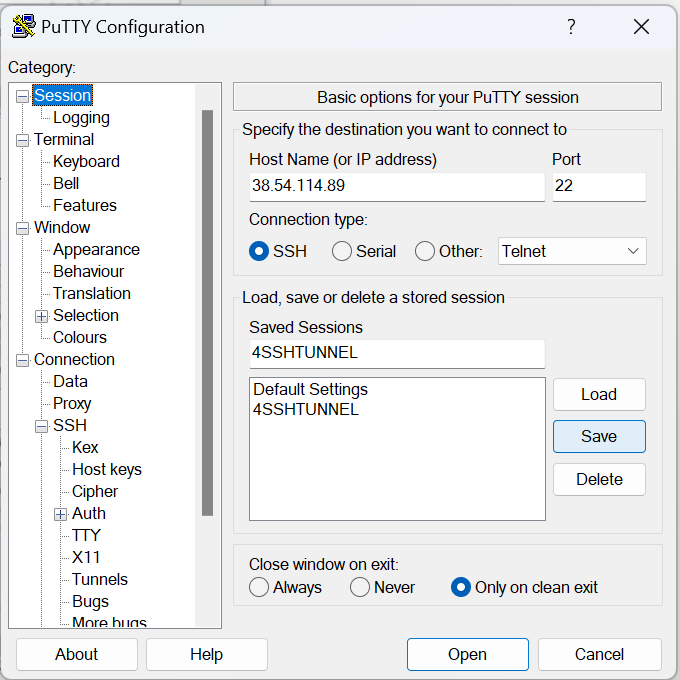
Here are the tools you need
- An android phone (You can use Apple/iPhone with torque pro, but the instructions here are for android)
- The Torque Pro app on the phone
- Prius PIDs for torque pro (Download here)
- A compatible OBD2 adapter, I use a WiFi adapter, you can use a Bluetooth or any other that works with torque pro
- A laptop with software like excel or LibreOffice calc, A paper and pen should also work
- A charger capable of charging a battery of 6 NIMH cells (Battery means in series), I use the SKYRC imax B6 mini (I don’t, I use my own home made charger built with an arduino, a acs712 current sensor, and a screen, but for the purpose of this tutorial, we need a charger so the imax B6 mini should do the trick)
- Car headlight lamps (To drain the batteries)
Like everyone else, it all started with CHECK HYBRID SYSTEM STOP THE VEHICLE IN A SAFE PLACE getting displayed on my center “multi information display / instrument panel” or MID for short.
Connecting the OBD2 adapter resulted in fault code (P0a80) other relevant codes might display with P0a80 such as p3011, p3012, p3013 etc. which should point you to the failing module pairs that are causing the failure. in my case, I only had the P0a80.
Prius battery terminology (As per Toyota)
Hybrid battery: the whole Prius traction battery pack of 28 modules
Module Pair: the car reads voltages of modules in pairs, So voltages of the 28 modules in a Prius battery are reported to the car as 14 values, meaning every 2 modules are read together as the sum of the voltage of those 2 modules.
Battery Module: in a Prius battery, every 6 cells are enclosed in a sealed container called a module, this is why you don’t directly see the cells, a module’s nominal voltage is 7.2, which is the nominal voltage of 1 cell multiplied by 6.
Battery Cell: A 1.2V NIMH cell that you will not see because it is hidden inside a module.
So, without further ado, let us get started
Diagnosis, which modules are bad
Before we take the battery out, we can save a hell lot of time by looking at what the car has to say about it’s battery pack.
I have broken this down to steps you see below
- Install torque pro to your phone (android in my case)
- Download the Prius 3rd Gen PIDs file by clicking here
- extract the file you have just downloaded to the (/.torque/extendedpids) directory in your phone
- Open torque pro, and go to the Menu -> Settings -> Manage extra PIDs/Sensors -> Menu -> Add predefined set.
- Create an Realtime Information page in torque pro to display battery voltages in real time such as the one below, you start with an empty page, then add (tiny) displays corresponding to voltages of individual modules, I personally like to add the Min and Max voltage entries to make it easier to know when you have found what you are looking for while driving without having to scan through the batteries
- Clear the error code, switch the car off then on again, the car should now appear to be working fine as if the battery is okay, this is obviously just for the test as the car will soon find out the problem again and inform you of your problem
- Now, once connected and information is displayed, find a nice uphill climb that is not too steep, with no traffic, at the bottom of that climb, floor the break and gas pedal at the same time, this will charge the battery, then on EV, start climbing wile recording your phone screen, the battery should drain really fast and you will either hear the engine running, or the “Check hybrid system” message should appear again, either way, you now have a reading of which batteries drained very fast…
- Inspect the recorded screen recording, and figure out which modules are the ones causing the problem, please note that there may be other modules in bad shape, but for now, the worst ones are clear
Taking the battery out of the car
To be able to pull the battery out of the car, you will need to take the following steps
Some theory
The 20% to 80%
Q: Why does the car consider the battery fully charged at 80%, and depleted at 20% of the batteries actual capacity ?
A- Why the 80% cap ?
Let us start with why it caps at 80% ! (At 80 percent, 100% will display on your instrument cluster)
The most common theory (that i don’t find convincing) is that the car wants to leave headroom for regenerative breaking, if it were so, why does it start using the gas engine’s breaking at 80% ? burning fuel, and defeating the purpose of regenerative breaking ?
My own theory is that there are multiple reasons, of which the headroom theory above is not one… here are the reasons i expect the car was designed this way
1- NIMH batteries heat up once you are charging above 80%, which is wasted energy, so the car is expected to try an use up the battery back down to the happy 6/8 area.
2- Heat is bad for the module’s health, and the health of the modules around it (See 1)
3- When modules in module pairs become mismatched health wise, this 20% headroom spares the weaker cell the overcharge and the damage associated with it., illustration will be added soon.
B- And the 20% depletion mark ?
NIMH cells can be depleted to ZERO, in fact, the company that makes the enelope batteries for Panasonic calls depleting the battery to zero and then charging it again a refresh function.
The area between 0.9V and zero volts has very little energy, as most energy is delivered between 1.3 and 1 volt, but still, this area is much less than 20% ! so why 20%
1- Unlike gas cars, hybrid vehicles do not have a 12V starter motor, the gas engine in a hybrid car is started by the electric motor itself, the same one used to propel the car is used to start the engine, if the battery falls below 20%, especially as batteries start to age, there will not be enough power to start the engine, more to that, the batteries have internal resistance, so the car needs to be sure that when it is parked for a few days (or months), it will have enough traction battery power to start the gas engine.